Smart Grid
Smart Grid
Smart
Grid
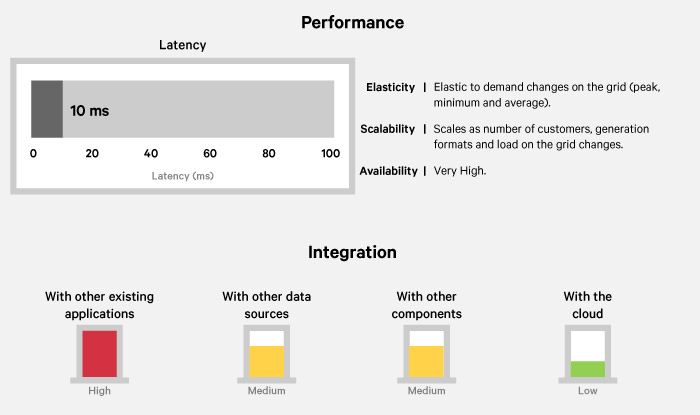
A Smart Grid has the ability to self-balance supply and demand of electricity, self heal, optimize for cost, manage intermittent power sources and provide a resilient, data driven, optimized and secure infrastructure.
Industries adopting this use case include
Smart City
Use Case Archetype
Data intensive
Human latency sensitive
Machine to machine latency sensitive: Use cases where services are optimized for machine-to-machine consumption. Because machines can process data much faster than humans, speed is the defining characteristic of this archetype.
Life critical
Edge Infrastructure Model

Device
Edge
location
Smart devices (e.g. in vehicle, street lamp, IoT)
no. of racks
0
power
Up to 1kW
Tenancy
Single Tenant
External environment
Controlled (within Device), Harsh & Rugged
Passive infrastructure
May or may not have power and filtration, no cooling etc.

Micro
Edge
location
Enterprise site (e.g. retail, factory floor, IT closet)
no. of racks
0 - 4 racks
power
Up to 20kW
Tenancy
Single Tenant
External environment
IT Closet, Commercial & Office, Harsh & Rugged
Passive infrastructure
Has power with limited cooling and filtration, etc.

Distributed Edge
Data Center
location
Enterprise site (e.g. warehouse, office), telecoms site, parking lot, tier 2/3 city
no. of racks
5 - 20 racks
power
Up to 200kW
Tenancy
Single Tenant / Multi-tenant
External environment
Harsh & Rugged, Commercial & Office, Conditioned & Controlled
Passive infrastructure
Tier 1+

Regional Edge
Data Center
location
Tier 2/3 city
no. of racks
20+ racks
power
Up to 4000kW
Tenancy
Multi-tenant
External environment
Conditioned & Controlled
Passive infrastructure
Tier 3+
Workload Characteristics